Charging Concept for High Voltage Battery Systems
Many applications involve the charging of high voltage battery systems. Most off the shelf battery chargers cannot handle the voltages involved. We show you how MEAN WELL power supplies can be used for this purpose.
Basically, this involves connecting multiple power supplies together in a ‘chain’ to achieve the required output voltage and current.
Choosing a Power Supply for Charging Batteries
You need to choose a power supply that has constant current limiting without shutting down when presented with anything that looks like an overload situation. The output current also needs to suit the batteries.
The following MEAN WELL power supplies have the required constant current limiting function:
|
Series |
Output Voltage Options |
Output Current |
|---|---|---|
|
RSP-750 |
5V, 12V, 15V, 24V, 27V, 48V |
100A (5V), 62.5A (12V), 50A (15V), 31.3A (24V), 27.8A (27V), 15.7A (48V) |
|
RSP-1000 |
12V, 15V, 24V, 27V, 48V | 60A (12V), 50A (15V), 40A (24V), 37A (27V), 21A (48V) |
|
RSP-2400 |
12V, 24V, 48V | 166.7A (12V), 100A (24V), 50A (48V) |
|
RSP-3000 |
12V, 24V, 48V | 200A (12V), 125A (24V), 62.5A (48V) |
|
RST-5000 |
24V, 48V | 200A (24V), 105A (48V) |
|
RST-10000 |
24V, 48V | 400A (24V), 210A (48V) |
As a rule of thumb, the charge current should be 10% of the AH capacity of the battery. For example, for a 200AH battery you would select a power supply with an output current of around 20A.
All power supplies in the chain should have the same current rating, and where possible the same model.
Voltage
Let’s presume that you want to charge a 144V, 200AH battery. In this instance your best solution would be to use 3 x MEAN WELL RSP-1000-48 power supplies.
This is because 3 x 48V = 144V.
Remember, if you need to use power supplies with different output voltages you must ensure the output currents of the power supplies are similar.
With the MEAN WELL power supplies, you can adjust the output voltage with the built-in potentiometer. So, you should be able to come up with a combination that gives the exact voltage requirements.
Connecting the Power Supplies in a Chain
Protecting the Power Supplies
It is strongly recommended that you use a blocking diode on the positive output terminal of the battery. This is to prevent the battery back-feeding into the power supplies. This diode must be capable of handling the full output current from the power supplies.
The following diagram shows how the power supplies in the chain should be connected to each other and the battery:
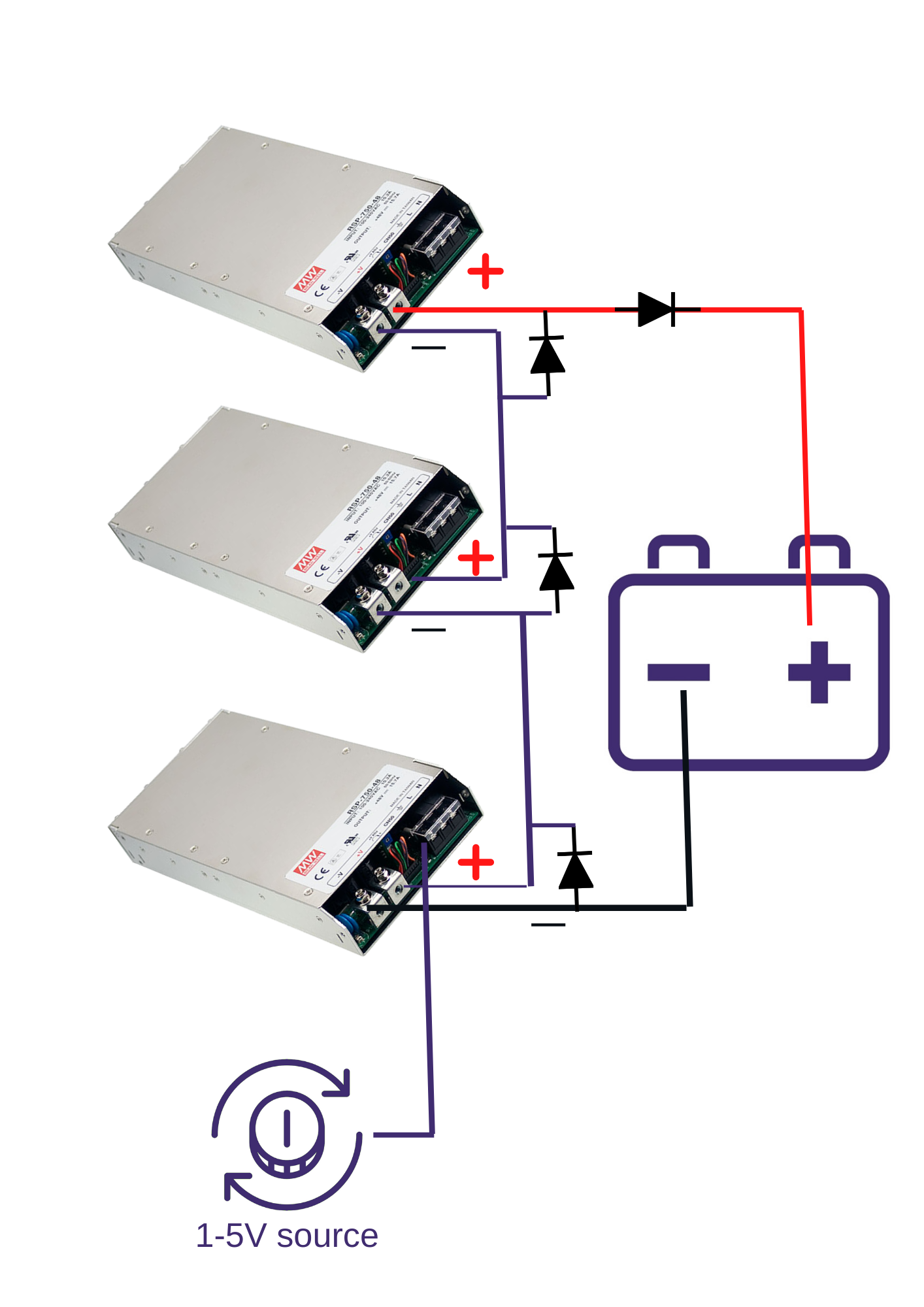
Place a reversed diode across the output of each power supply in the chain to prevent reverse voltage. This diode only needs to be relatively small, say 10% of the rated current of the power supplies.
The remote programming input on the first power supply in the chain is the only one at ground potential. This power supply is acting as the negative terminal in the string. Use its programming input to adjust the output voltage with an appropriate 1-5V signal, so that the positive output of the last power supply in the chain delivers the correct float/boost voltage.
The other power supplies in the chain will have their remote programming input floating at the combined voltage of the output of the power supplies further down the chain, so it is not practical to use the programming input on these power supplies.
Technical Support and Advice
If you have any questions about implementing the above solution, do not hesitate to contact ADM. A member of our technical team will gladly answer any questions you may have.
IS THIS INFORMATION USEFUL?
If so, why not share it with your peers and colleagues. Simply click on the blue LinkedIn share icon below.


